You must have seen a red colored small cylinder hanging on a wall place at highly identifiable location in your school, college, office or any workplace. That red cylinder is called fire extinguisher, these are mandatory safety equipment to keep in places of potential fire hazards, in the hands of a rightly trained man fire extinguishers can save people and property from fire in its early stages. If you are an engineer or a safety office you might know about this piece of equipment but most of us don’t know much details about the widely used fire extinguishers, types of fire extinguishers, selection of fire extinguishers and its inspection requirements.
What is a Fire Extinguisher?
A fire extinguisher is a small, portable, movable and active piece
of equipment use to extinguish or prevent small accidental fires. Fire
extinguisher can control small fires in emergency conditions however, they
shouldn’t be used on out of control fires. A fire extinguisher is a small
cylindrical vessel containing a special material that can extinguish of control
the fire when that material is directed onto the fire. This substance has an
ability to control a fire that is spread on a small area. Fire Extinguisher is
like a first aid against accidental fires. A personal can easily operate this
device. Non cylindrical fire extinguishers are very less common.
Parts of a Fire Extinguisher
Almost all the fire extinguishers are consisting of similar type
of parts, although the extinguishing agent which is filled inside the fire
extinguisher may differ depending upon the type of fire and fire origin. Common
parts are:
- A cylindrical pressurized vessel that contains the fire extinguishing agent.
- A release mechanism consisting of a squeeze and release handle, valve assembly, pressure gauge.
- A safety mechanism consisting of a seal and a safety pin.
- A hose with a nozzle for directing extinguishing agent to fire.
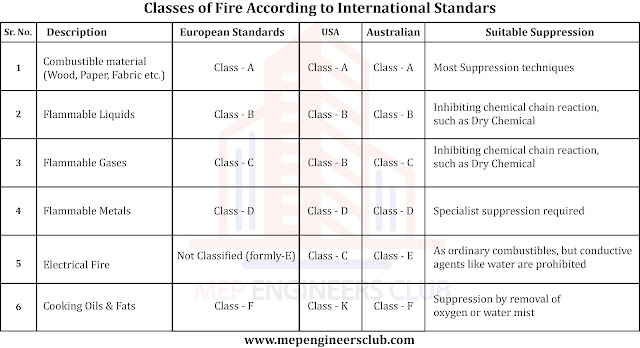
Classes of Fire Extinguisher
Before selecting or installing a fire extinguisher it is very
important to know about its characteristics, different types of fires require
different type of extinguishing agents. So, on this bases fire extinguishers
are classified into 6 categories.
Class A
These fire extinguishers are used to put out Class A fires like
ordinary combustible materials such as wood, cloth, paper, fabric, rubber and
many plastics.
Class B
These fire extinguishers are used to put out Class B fires in
flammable and combustible liquids, petroleum
greases, tars, oils, oil-based paints, solvents, lacquers, alcohols.
Class C
These fire extinguishers are used to put out Class C fire hazards
that involve fires caused by combustion of gases such as methane, propane,
hydrogen, acetylene, natural gas and city gas.
Class D
These fire extinguishers are used to put out Class C fire in combustible metals, such as
magnesium, titanium, zirconium, sodium, lithium, and potassium.
Class E
These fire extinguishers are used to put out Class E fires that
involve energized electrical equipment. However, in many countries it is termed
as Electrical fire class not Class E and was formally classified as Class C.
Class F
Class F fire extinguishers find their use to extinguish class F
fires characterized by fires from combustible cooking media such as cooking
oils, vegetable oils, fats, butter, etc. In some standards it is termed as
Class K rather than Class F.
Note that, the above fire extinguisher classes may slightly differ
from country to country. The comparison is tabulated below for guidance:
Types of Fire Extinguishers
Depending on the type of extinguishing content in inside the
vessel, 7 types fire extinguishers are available.
These are:
- · Water Fire Extinguisher
- Foam Fire Extinguisher
- Powder Fire Extinguisher
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Fire Extinguisher
- Wet Chemical Fire Extinguisher
- Dry Chemical Fire Extinguisher
- Clean Agent Fire Extinguisher
Water Fire Extinguisher
Water is used as primary extinguishing liquid in these types
of fire extinguishers with other additives. This is the most economic and simplest
fire extinguisher amongst all. These are suitable to control and putt off class
A type fires, they have bright red label on them. Water fire extinguishers are
widely used in homes, shops, offices, retail stores, schools, warehouses and
hospitals etc. A drawback of these water fire extinguishers is that it cannot
be used in freezing conditions.
Water type fire extinguishers are of four types.
- Water Jet Extinguishers
- Water Spray Extinguishers
- Water Extinguishers with additives
- Water mist Extinguishers
Water jet extinguisher throws a water jet at the burning
medium forcing the material to cool down. Water spray extinguishers uses a fine
spray such that it suspends in the air around the fire preventing from further
expansion. A foaming chemical is added in the water fire extinguishers with
additives that help in effective soaking into the burning materials.
Water mist fire extinguisher applies fine droplets of fog or mist. Due to this
mist these droplets have more surface area hence covering more burning area,
quickly evaporating and removing the heat energy from the fire.
Foam Fire Extinguisher
AFFF (aqueous film-forming foam) and FFFP (film-forming
fluoroprotein) fire extinguishers are rated for use on both Class A and Class B
fires. Foam fire extinguishers blanket the fire with a foam generated when the
spray hits the air. This blanket of foam prevents the fire from further spread
and vapors reaching the air, also the water in the foam acts as a cooling agent
to minimize the possibility of re-ignition. Foam fire extinguishers carry a
cream label.
Powder Fire Extinguisher
Power fire extinguishers are multi-purpose and are commonly
known as ABC extinguishers as they can be utilized in the event of a class A, B
or C fire scenario. However, this type of extinguisher should not be used in an
enclosed space. This is because the powder can be easily inhaled and is very
difficult to clean up after the fire has been extinguished.
Fine chemicals in powder form as extinguishing agents are
released by the powder extinguishers to blanket the fire and suffocate it. The
common powder is mono-ammonium phosphate. Powder fire extinguishers carry a
blue label.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Fire Extinguisher
Carbon dioxide (CO2) fire extinguishers are used
for electrical hazards. The principal advantage of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) fire
extinguishers is that the agent does not leave a residue after use. This can be
a significant factor where protection is needed for delicate and costly
electronic equipment. Carbon dioxide extinguishers are listed for use on Class
B and Class C fires.
Carbon dioxide fire extinguishers blanket the fire by
cutting off the air supply which in turn removes oxygen, required for fire to
continue. CO2 fire extinguishers carry a black label.
Wet Chemical Fire Extinguisher
The wet chemical extinguishers are highly efficient
extinguishers and ideal for fire hazards
involving cooking oils and vegetable fats (Type F or type K fire class). The
liquid agent has a PH of 9.0 or less. They contain a potassium solution that
rapidly knocks the flames out, cools the hot oil, and seals the liquid surface
with a thick soap-like substance generated by a chemical reaction. This
soap-like substance prevents re-ignition. Wet chemical fire extinguishers can
also be used for class A fires and they carry a yellow label.
Clean Agent Fire Extinguisher
Clean fire extinguisher is a gaseous fire suppression
system. The extinguishing agent is stored as a liquid in the cylindrical vessel
but it converts to an eco-friendly, non-conductive, gas when it comes in
contact with the air. This gas then makes a blanket around the fire reducing
the oxygen levels. These fire extinguishers are widely used for Class B and
E-type fire.
The following table will provide an overview of fire extinguisher type chart:
Selection of Fire Extinguisher
While selecting a fire extinguisher, the engineer must identify the reason of fire and its origin so that class of the fire could be determined. If the fire hazard is a mix of 2 or 3 fire classes, it is important to select a fire extinguisher that can drop off all the present hazards.
The manufacturers provide the rating for the extinguisher and that is specified on the product label affixed to the extinguisher. The main factors that should be considered while selecting a fire extinguisher are:
- Fire Extinguishers of certain fire hazard types may not be effective against fires of a different hazard class. Even, it may increase the fire severity if not selected carefully.
- Extinguishers intended for certain types of hazards can increase personnel hazards for users when used against different hazard class fires.
- Extinguishers rated for multiple fire hazards may have different levels of effectiveness for each hazard.
- Fires involving metals are controlled by class D extinguishers. Note that, an extinguisher that may be highly effective in one type of metal fire, may be dangerous on other types of metallic fires.
- Class F (K) fire extinguishers for controlling kitchen fire exposures may not be suitable for conventional usage.
Fire Extinguisher Inspection
NFPA 10 provides guidelines for the inspection requirements
of fire extinguishers, to get to know if fire extinguisher will work properly during
fire events. This inspection is carried out by certified safety professionals, performing
an inspection is the easiest thing you can do to ensure your extinguisher can
be used reliably and effectively in an emergency. At a minimum, inspection
needs to consist of the following steps:
- Availability: Make sure it is located at designated place and can be easily accessible, and visible.
- Physical State: Make your fire extinguisher is physically intact, there is no damage, clogged nozzle, handle is operational, tamper seal in unbroken, locking pin is intact, and operating instructions are visible.
- Pressure Gauge & Weight: Inspect the pressure gauge and weight of the fire extinguisher by ensuring that the gauge is at operable range and vessel is full. For wheeled extinguishers check the wheels on the trolley, nozzle and hose.
- Inspection Tag: Ensure that inspection tag on fire extinguisher is filled and extinguisher is being properly inspected.
Any observation should be informed
to the concerned person for necessary action and a report must be prepared indicating
the date of inspection. Such fire extinguisher inspection reports must be maintained
for at least 12 months. Depending on the type of extinguisher, an internal
examination of fire extinguishers must be conducted within 1-6 year intervals.








0 تعليقات
Please avoid posting spam links in the comment section.